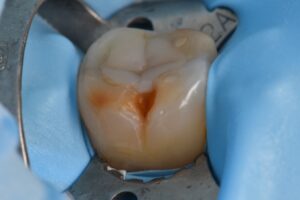
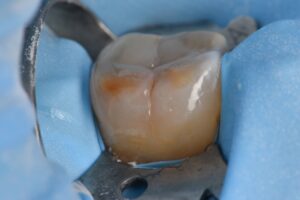
Molar hypomin presents a situation of compromised flexural/tensional resistance in posterior teeth and often hairline fractures can feed an already susceptible base, inducing rapid caries formation.
Interestingly, self-etching/MDP-based adhesive monomers did not show a significant advantage over etch-and-rinse adhesives. To enhance bonding further, sodium hypochlorite can be applied to the surface “after etching” to enhance the shear bond strength further. In this situation, the spongy, collagen-rich layer is reduced first (obviating the need for sodium hypochlorite) and the surface is micro air abraded (29 micron aluminum oxide) before the etching step, 2% CHX (aq) and bonding. Microlayers anchor the hybridization, and voila, you have solid adhesion.
Lagarde M, Vennat E, Attal JP, Dursun E. Strategies to optimize bonding of adhesive materials to molar-incisor hypomineralization-affected enamel: A systematic review. Int J Paediatr Dent. 2020 Jul;30(4):405-420. doi: 10.1111/ipd.12621. Epub 2020 Feb 12. PMID: 31990108.
#KerrSimplishade #MolarHypomin #BondingtoHypomin